Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (11): 1798-1804.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.11.029
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain relief in knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis
Ding Xiang, Zhang Yi, Deng Zhen-han, Yang Ye, Yang Tuo, Li Hui, Lei Guang-hua
- Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
-
Revised:2015-01-15Online:2015-03-12Published:2015-03-12 -
Contact:Lei Guang-hua, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Ding Xiang, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81272034; the Project of the Development and Reform Commission of Hunan Province, No. [2013]1199; the Scientific Research Project the Science and Technology Commission of Hunan Province, No. 2013SK2018; Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China, No. 20120162110036
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Xiang, Zhang Yi, Deng Zhen-han, Yang Ye, Yang Tuo, Li Hui, Lei Guang-hua. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain relief in knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1798-1804.
share this article
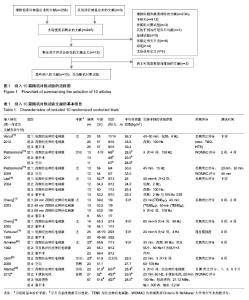
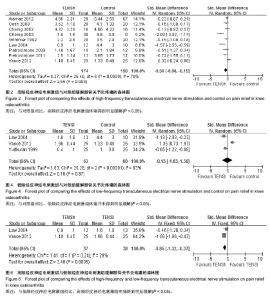
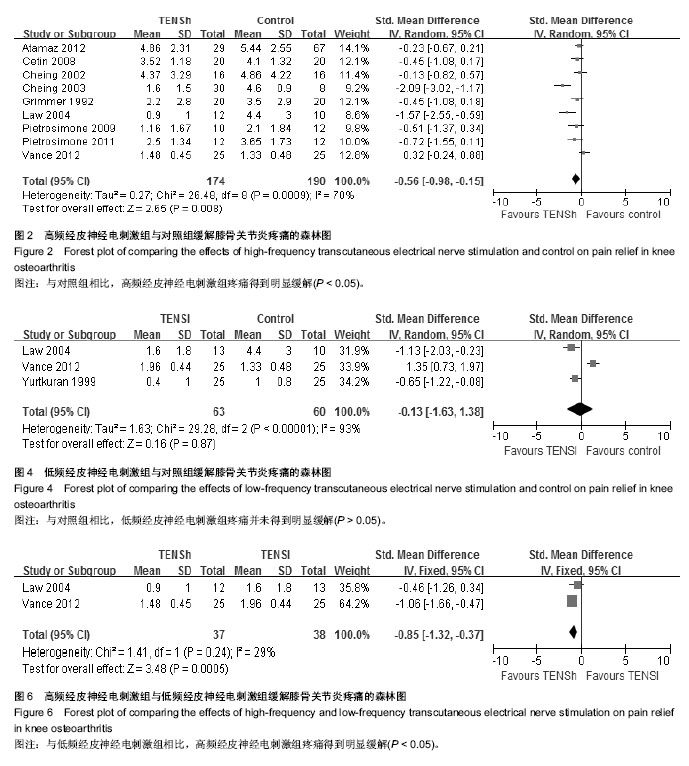
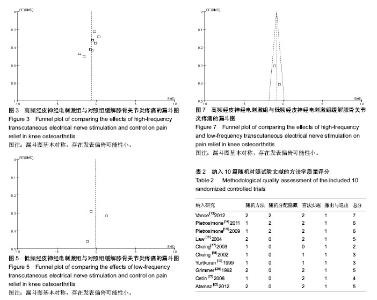
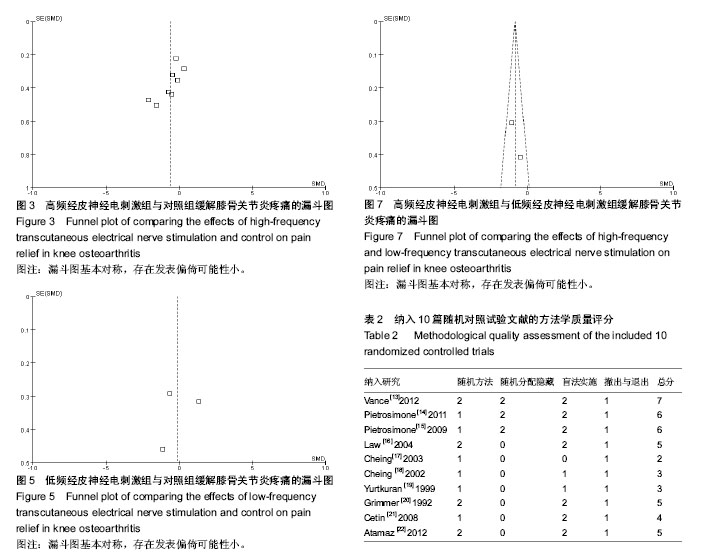
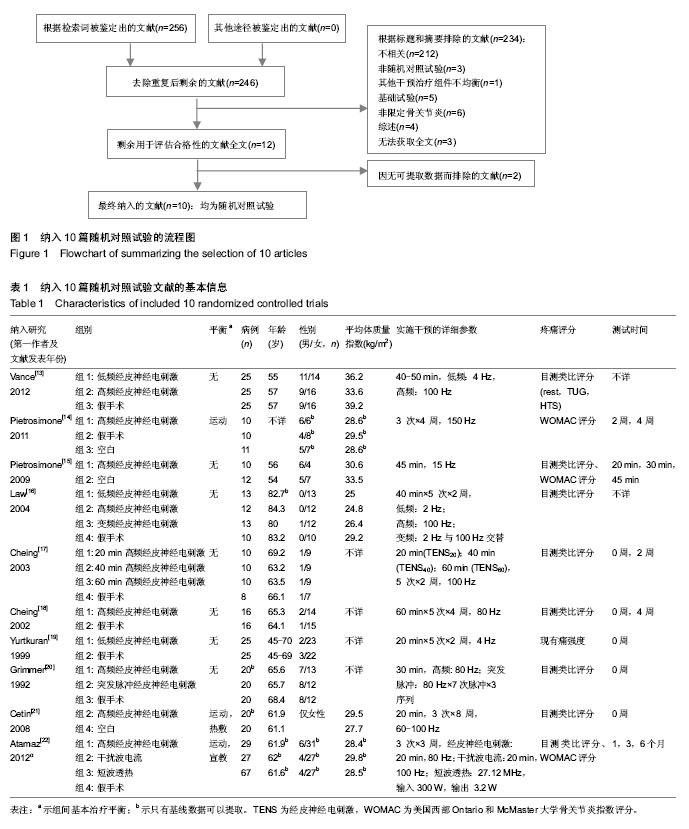
2.1 纳入文献的基本流程 通过PubMed,Embase和Cochrane数据库共检索出256篇题录,通过标题和摘要共排除234篇。经全文筛查最终纳入10篇文献[13-22],均为英文文献,10项研究均为随机对照试验。本研究文献纳入流程图见图1。 2.2 纳入文献的基本资料和方法学质量评价 表1为纳入文献的基本信息。10篇文献均为英文文献。采用改良Jadad量表对10项研究的方法学质量进行评价,总分1-3分为低质量研究,4-7分为高质量研究,评价结果显示7项研究为高质量研究,另外3项为低质量研究,见表2。 2.3 荟萃分析结果 纳入的10项研究以患者疼痛的主观评分为结局指标比较组与组之间对缓解膝骨关节炎疼痛症状的差异。结果显示高频经皮神经电刺激组与对照组间差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.56,95%CI(-0.98,-0.15),P=0.008,I2=70%],低频经皮神经电刺激组与对照组间差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.13,95%CI(-1.63,1.38),P=0.87,I2=93%],高频经皮神经电刺激组与低频经皮神经电刺激组间差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.85,95%CI(-1.32,-0.37),P=0.000 5,I2=29%],见图2-7。结果表明高频经皮神经电刺激能有效缓解膝骨关节炎患者的疼痛症状,而低频经皮神经电刺激对缓解此症状无明显疗效。漏斗图基本对称,无明显异常点,判定存在发表偏倚的可能性较小。"
| [1] Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of OA. Classification of Osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986; 29: 1039-1049. [2] Peat G, McCarney R, Croft P. Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: a review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60(2): 91-97. [3] Maurer K. Basic data on arthritis: knee, hip and sacroiliac joints in adult aged 25-74 years. United States, 1971-1975. Hyattsville MD, National Centers for Health Statistics, 1979, Vital and Health Statistics, No. 213. [4] Jones A, Doherty M. ABC of Rheumatology: osteoarthritis. BMJ. 1995; 310: 457-460. [5] Walker-Bone K, Javaid K, Arden N, et al. Regular review: medical management of osteoarthritis. BMJ. 2000; 321(7266): 936-940. [6] Hunter DJ, Felson DT. Osteoarthritis. BMJ. 2006; 332(7542): 639-642. [7] Sluka KA, Walsh D. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: Basic science mechanisms and clinical effectiveness. J Pain. 2003; 4(3):109-121. [8] Electrotherapy Standards Committee: Electrotherapeutic terminology in physical therapy (report). Section on clinical electrophysiology and American Physical Therapy Association, Alexandria, VA, 2001. [9] Melzack R, Wall PD. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science. 1965; 150:971-978. [10] Robinson AJ, Snyder-Mackler L. Clinical Electrophysiology: Electrotherapy and Electrophysiological Testing (2nd edition). Baltimore, MD, Williams and Wilkins, 1995. [11] Walsh D. TENS: Clinical Applications and Related Theory. Edinburgh, UK, Churchill Livingstone, 1996. [12] Osiri M, Welch V, Brosseau L, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for knee osteoarthritis. Chochrane Data Base Syst Rev. 2001. [13] Vance CT, Rakel BA, Blodgett NP, et al. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Pain, Pain Sensitivity, and Function in People With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys Ther. 2012; 92(7): 898-910. [14] Pietrosimone BG, Saliba SA, Hart JM, et al. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation and Therapeutic Exercise on Quadriceps Activation in People With Tibiofemoral Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011; 41(1):4-12. [15] Pietrosimone BG, Hart JM, Saliba SA, et al. Immediate Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation and Focal Knee Joint Cooling on Quadriceps Activation. Med Sci Sports Exer. 2009; 41(6): 1175-1181. [16] Law PP, Cheing GL. Optimal Stimulation Frequency Of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation On People With Knee Osteoarthritis. J Rchabil Med. 2004; 36:220-225. [17] Cheing GL, Tsui AY, Lo SK, et al. Optimal stimulation duration of tens in the management of osteoarthritic knee pain. J Rehabil Med. 2003; 35:62-68. [18] Cheing GL, Hui-Chan CW, Chan KM. Does four weeks of TENS and/or isometric exercise produce cumulative reduction of osteoarthritic knee pain? Clin Rehabil. 2002; 16(7):749-760. [19] Yurtkuran M, Kocagil T. TENS, electroacupuncture and ice massage: comparison of treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee. Am J Acupunct. 1999; 27(3/4):133-140. [20] Grimmer K. A conlrolled double blind study comparing the effects of strong Burst Mode TENS and High Rate TENS on painful osteoarthritic knees. Aust J Physiother. 1992; 38(1): 49-56. [21] Cetin N, Aytar A, Atalay A, et al. Comparing Hot Pack, Short-Wave Diathermy, Ultrasound, and TENS on Isokinetic Strength, Pain, and Functional Status of Women with Osteoarthritic Knees. Am J Phys Med. 2008; 87(6):443-451. [22] Atamaz FC, Durmaz B, Baydar M, et al. Comparison of the Efficacy of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, Interferential Currents, and Shortwave Diathermy in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93:748-756. [23] 卢亮宇, 王宇彬. 膝骨关节炎疼痛机制及治疗研究现状[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2007, 26(4):512-516. [24] Wyke B. The neurology of joints: a review of general princibles. Clin Rheum Dis. 1981; 7:233-239. [25] Kidd BL, Gilson SJ, Mapp PI, et al. Neuropeptides as mediators of inflammation and chronic pain. Eur J Rheumatol Inflam. 1991; 11:47-65. [26] Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Phys. 2007; 213(3):626-634. [27] Melzack R, Wall PD. Pain mechanism, a new theory. Science. 1965; 150:971-979. [28] Palmer ST, Martin DJ, Steedman WM, et al. Effects of electric stimulation on C and A delta fiber-mediated thermal perception thresholds. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85: 119-128. [29] Fields HL, Basbaum AI. Central nervous system mechanisms of pain modulation, in Wall PD, Melzack R (eds): Textbook of Pain, chap 12. New York, NY, 1999: 243-257. [30] Taylor P, Hallett M, Flaherty L. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Pain. 1981; 11(2):233-240. [31] Smith CR, Lewith GT, Machin D. TNS and osteo-arthritic pain. Preliminary study to establish a controlled method of assessing transcutaneous nerve stimulation as a treatment for the pain caused by osteo-arthritis of the knee. Physiotherapy. 1983; 69(8):266-268. [32] Lewis D, Lewis B, Sturrock RD. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in osteoarthrosis: a therapeutic alternative? Ann Rheum Dis. 1984; 43(1):47-49. [33] Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines. Owteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008; 16(2): 137-162. [34] Woolf CJ, Mitchell D, Barrett GD. Antinociceptive effect of peripheral segmental electrical stimulation in the rat. Pain. 1980;8:237-252. [35] Campbell JN, Taub A. Local analgesia from percutaneous electrical stimulation. Arch Neurol. 1973;28:347-350. [36] Janko M, Trontelj JV. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation a microneurographic and perceptual study. Pain. 1980;9:219-230. [37] Lee KH, Chung JM, Willis WD. Inhibition of primate spinothalamic tract cells by TENS. J Neurosurg. 1985;62: 276-287. [38] Sluka KA, Deacon M, Stibal A, et al. Spinal blockade of opioid receptors prevents the analgesia produced by TENS in arthritic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289: 840-846. [39] Kalra A, Urban MO, Sluka KA. Blockade of opioid receptors in rostral ventral medulla prevents antihyperalgesia produced by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;298:257-263. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [4] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [5] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [6] | Zhu Shi-bai, Zhai Jie, Jiang Chao, Ye Can-hua, Chen Xi, Weng Xi-sheng, Qian Wen-wei. Application of “enhanced recovery after surgery” in the perioperative period of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 456-463. |
| [7] |
Gao Wei-lu, Li Hong, Liu Bi-quan, Hu Yong, Liu Jing-jun, Yin Li, Liu Hu, Mei Bin, Yin Zong-sheng.
Analgesic effect of femoral and sciatic nerve block under multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty
|
| [8] | Bai Zhao-hui, Zhang Ying, Yin Qing-shui, Xia Hong, Wang Jian-hua, Xu Jun-jie. Navigational template applied in the orthopaedic field in China: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3023-3030. |
| [9] | Liu Sheng-fa, Zhang Feng. Kinesio taping combined with manual lymphatic drainage for lower limb swelling after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1647-1651. |
| [10] | Ma Lu-yao, Guo Wan-shou, Ma Jin-hui, Yue De-bo. Does a fixed distal femur resection angle influence radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasty? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1658-1663. |
| [11] | Zhang Song, Zhang Tao, Yang Jian-wen, An Min, Tang Ben-sen. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid on blood loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1681-1687. |
| [12] | Mei Gao-chang, Li Yuan-hai. Protection of pre-administration of Shengmai injection on ischemia-reperfusion injury of skeletal muscle in lower limb after knee joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7917-7924. |
| [13] | Chen You-rong, Wan Fu-yin, Guo Wan-shou, Wang Wei-guo, Cheng Li-ming, Zhang Qi-dong, Ding Ran. Common peroneal nerve injury after primary total knee arthroplasty: risk factors and strategies of prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 8043-8050. |
| [14] | Ren Rong, Li Ling-wei, Guo Qi-fa. Feasibility of implantation of a cemented femoral stem in the treatment of osteoporotic femoral neck fracture in elderly patients: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7261-7266. |
| [15] | Chen Qun-qun, Chen Jian-fa, Zhou Chi, Dong Lu-jue, Huo Shao-chuan, Wang Hai-bin. Blood loss in primary total knee replacement with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid and presurization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6564-6569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||